Laser Bioanalytics uses lasers to process and sample tissue for biomedical analysis. Pulsed infrared and ultraviolet lasers are focused to small spots with high energy to remove selected regions with high precision. Under the proper conditions, large biomolecules such as proteins, DNA, and RNA can be removed while maintaining their structure and function which can be probed using a variety of analysis methods.
Infrared Laser Ablation
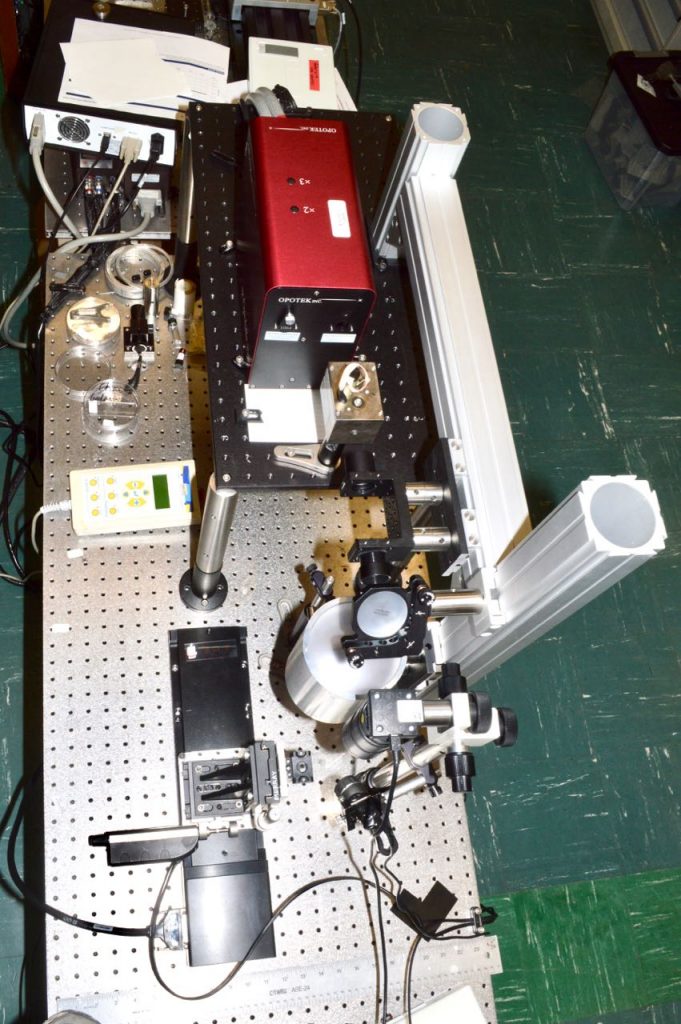
Tissue microdissection can be accomplished using a focused infrared laser that excites water molecules in thin sections of tissue causing the explosive release of material from small regions of interest. The collected material can be analyzed by mass spectrometry and other methods.
- S.-G. Park, K.K. Murray, Ambient laser ablation sampling for capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 27 (2013) 1673–1680. doi:10.1002/rcm.6618.
- F. Donnarumma, K.K. Murray, Laser ablation sample transfer for localized LC-MS/MS proteomic analysis of tissue, J. Mass Spectrom. 51 (2016) 261–268. doi:10.1002/jms.3744.
- K. Wang, F. Donnarumma, S.W. Herke, C. Dong, P.F. Herke, K.K. Murray, RNA sampling from tissue sections using infrared laser ablation, Anal. Chim. Acta. 1063 (2019) 91–98. doi:10.116/j.aca.2019.02.054.
Deep Ultraviolet Laser Ablation
Ultraviolet lasers can be focused to a small spot size due to their short wavelength. Deep UV light is strongly absorbed by tissue which results in clean cuts when used for LASIK eye surgery. The clean cut also makes this wavelength ideal for tissue microdissection.

- R.O. Lawal, L.T. Richardson, C. Dong, F. Donnarumma, T. Solouki, K.K. Murray, Deep-ultraviolet laser ablation sampling for proteomic analysis of tissue , Anal. Chim. Acta , 1184 (2021).
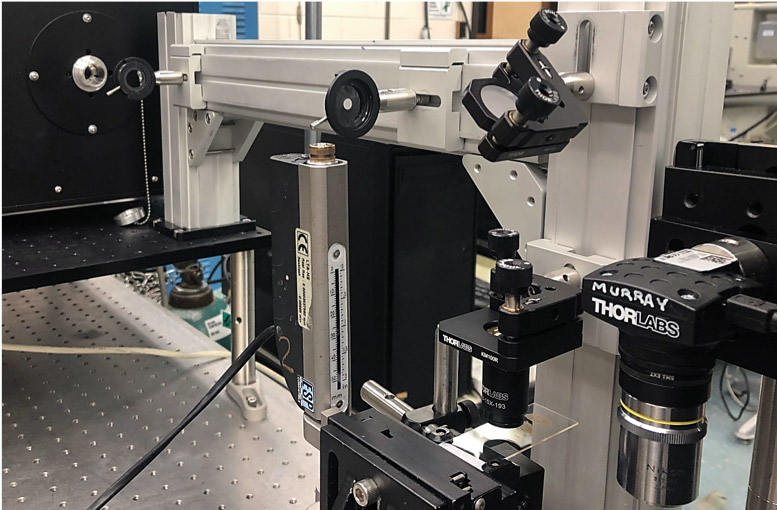
Near-field Laser Ablation
A pulsed laser can be combined with an atomic force microscope (AFM) for tissue microdissection with ultrahigh precision. The visible light laser is focused by interaction with a gold AFM tip which forms a crater in the surface.
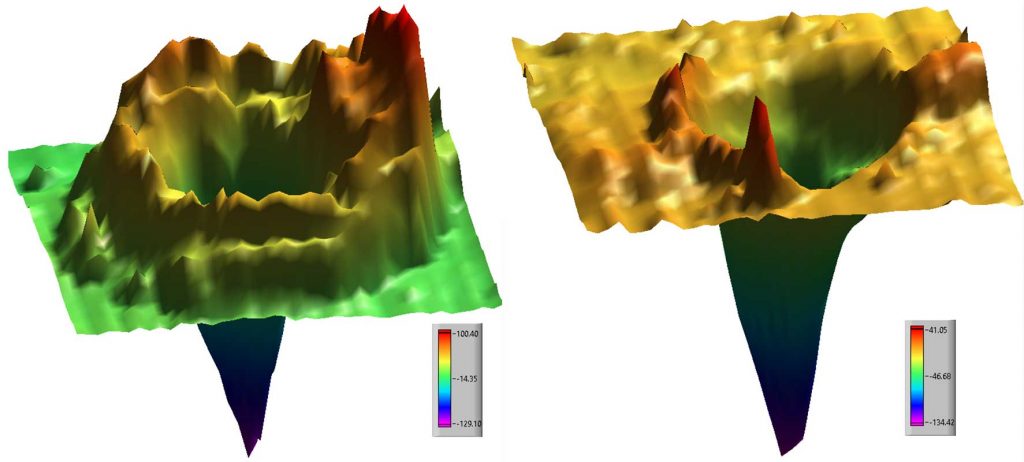
- S. Ghorai, C.A. Seneviratne, K.K. Murray, Tip-enhanced laser ablation sample transfer for biomolecule mass spectrometry, J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 26 (2015) 63–70. doi:10.1007/s13361-014-1005-x.
- F. Cao, F. Donnarumma, K.K. Murray, Wavelength dependent atomic force microscope tip-enhanced laser ablation, Appl. Surf. Sci. 447 (2018) 437–441. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.03.239.
- F. Cao, F. Donnarumma, K.K. Murray, Tip-enhanced laser ablation and capture of DNA, Appl. Surf. Sci. 476 (2019) 658–662. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.01.104.
Patents
- Murray, Kermit, K., Ghorai, S., & Seneviratne Chinthaka, A. Tip enhanced laser assisted sample transfer for biomolecule mass spectrometry (2018); Louisiana State University, assignee; US Patent No. US 10107835 B2.
- Murray, Kermit, K., & Banstola, Bijay, K. Devices and methods for MAI ionization (2020); Louisiana State University, assignee; US Patent No. US 10535508 B2.
- Murray, Kermit, K., Donnarumma, F., & Lawai, O. Devices and methods for deep UV laser ablation (2021); Louisiana State University, assignee; US Patent No. US 11094518 B2.
- Murray, Kermit, K., Donnarumma, F., & Stephenson, J. Methods and devices for sample capture using gas-pulse nanoparticle displacement (2022); Louisiana State University, assignee; US Patent No. US 11371913 B2.